Enzyme Lab With Liver Answers
Name:________________________________________ Appointment:__________
Investigation: Enzymes
Objectives
- Measure the effects of changes in temperature, pH, and enzyme concentration on reaction rates of an enzyme
- Explain how environmental factors affect the charge per unit of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
INTRODUCTION: What would happen to your cells if they made a poisonous chemical? You might remember that they would dice. In fact, your cells are ever making poisonous chemicals. They do not die because your cells use enzymes to intermission downwardly these poisonous chemicals into harmless substances. Enzymes are proteins that speed up the charge per unit of reactions that would otherwise happen more slowly. The enzyme is non altered by the reaction. You lot have hundreds of different enzymes in each of your cells.
Each of these enzymes is responsible for i detail reaction that occurs in the prison cell. In this lab, you volition study an enzyme that is found in the cells of many living tissues. The proper noun of the enzyme is catalase; it speeds up a reaction which breaks down hydrogen peroxide, a toxic chemic, into 2 harmless substances--water and oxygen. Lite can likewise break downward H2O2 which is why the chemic is sold in night containers.
The reaction is: 2H2Oii → 2HtwoO + O2
This reaction is important to cells considering hydrogen peroxide is produced as a byproduct of many normal cellular reactions. If the cells did non suspension downwards the hydrogen peroxide, they would be poisoned and die. In this lab, you will study the catalase institute in liver cells. You volition be using chicken or beef liver. Information technology might seem strange to use dead cells to study the function of enzymes. This is possible considering when a cell dies, the enzymes remain intact and active for several weeks, as long as the tissue is kept refrigerated.
| MATERIALS: | | | |
Function A - Detect Normal Catalase Reaction
i. Identify nigh ii ml of the 3% hydrogen peroxide solution into a clean test tube.
2. Using forceps and scissors cut a small piece of liver and add it to the examination tube. Push button it into the hydrogen peroxide with a stirring rod. Discover the bubbles.
What gas is beingness released? (consider the equation above) _____
Throughout this investigation you will estimate the rate of the reaction (how rapidly the solution bubbles) on a scale of 0-5 (0=no reaction, ane=slow, ..... 5= very fast). Assume that the reaction in step 2 proceeded at a rate of "four"
Remember that a reaction that absorbs heat is endothermic; a reaction that gives off estrus is exothermic. Feel the temperature of the exam tube with your mitt.
Has it gotten warmer or colder? _____________________
Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? _____________________
3. Pour off the liquid into a second test tube.
Assuming the reaction is consummate, what is this liquid composed of? __________________
What do y'all recollect would happen if y'all added more than liver to this liquid? ______________________
Test this and record the reaction charge per unit. Reaction Rate ___________ (1 – five)
4. Add another 2ml of hydrogen peroxide to the liver remaining in the kickoff test tube. What is the reaction rate? ____
Synthesis -- Answer the question: Is catalase reusable?
Merits :
Evidence
REASONING .
Part B - What Tissues Contain Catalase?
You will now exam for the presence of catalase in tissues other than liver. Place 2 ml of hydrogen peroxide in each of 3 make clean test tubes so add each of the three exam substances to the tubes. Equally you add each test substance, record the reaction charge per unit (0-5) for each tube.
| Substance | Apple tree | Potato | Yeast |
| Rate of Reaction (0-5) |
 Synthesis -- Do all living tissues contain catalase?
Synthesis -- Do all living tissues contain catalase?
Claim:
Evidence:
Reasoning:
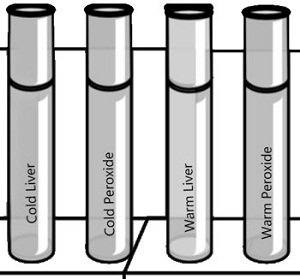
PART C - What is the Effect of Temperature on Catalase Activity?
i. Put a piece of liver into the bottom of a make clean test tube and cover it with a pocket-size amount of water. Place this examination tube in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes.
2. Remove the test tube from the hot water bath, allow it to air cool, then cascade out the water. Add 2 ml of hydrogen peroxide. Circumspection: Utilize a test-tube holder for hot test tubes.
What is the reaction charge per unit for the boiled liver and peroxide? __________
iii. Put equal quantities of liver into ii clean exam tubes and 1 ml HtwoO2 into 2 other exam tubes. Put one test tube of liver and ane of H2O2 into an ice bath. Place the other prepare in a warm h2o bathroom (not humid).
After iii minutes, pour each tube of H2Otwo into the corresponding tube of liver and observe the reaction
What is the reaction rate for the cold liver/peroxide? _____
What is the reaction charge per unit for the warm liver/peroxide? ____
Synthesis -- How does temperature touch on the catalase enzyme?
Merits:
Evidence:
Reasoning:
PART D - What is the Effect of pH on Catalase Activity
one. Add together 2 ml hydrogen peroxide to four clean examination tubes, then add:
Tube 1 – add iii drops of acetic acrid (vinegar) pH =_______
Tube 2 – add 3 drops of sodium bicarbonate (base of operations) pH =______
Tube three – add 3 drops of water (neutral) pH =_____
Tube four -- add iii drops of 1M NaOH pH = _____
Now add liver to each of the examination tubes (try to do it all at about the same time, so you can hands compare)
Rate of Reaction for:
Strong Acid (HCL) ____ Acid _____ Neutral ______ Base_____ Stiff base of operations (NAOH) _____
1. How does pH affect the reaction rate of catalase? Propose a way torefine your experiment to find theexact, or OPTIMAL pH and temperature of catalase.
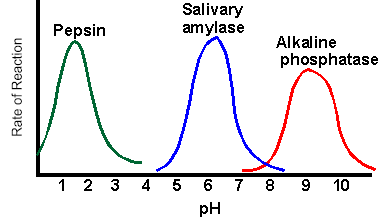
2. The following graph shows reaction rates of various enzymes in the body. Pepsin is found in the stomach, amylase in the saliva, and phosphatase in the liver.
Synthesis: How does pH touch on the activeness of enzymes?
Merits:
Evidence:
Reasoning:
Part Eastward - Blueprint an Experiment

Lactaid is a product designed to aid people who cannot digest milk sugar (lactose) because they are missing the enzyme lactase. Many people are lactose-intolerant, a condition that is mainly genetic. Lactase breaks downwards lactose into two subunits: glucose and galactose.
To test for the presence of monosaccharides and reducing disaccharide sugars in nutrient, the food sample is dissolved in water, and a pocket-size corporeality of Benedict's reagent is added. The solution should progress in the colors of blue (with no glucose present), green, xanthous, orange, reddish, and then brick red when there is a large corporeality of glucose present. (Google bridegroom'southward exam to see the fashion this looks.)
Design an experiment where you would determine how quicly lactaid works to pause downward milk sugar at dissimilar temperatures.. Be specific in your clarification, employ drawings if necessary.
Enzyme Lab With Liver Answers,
Source: https://www.biologycorner.com/worksheets/enzyme_lab.html
Posted by: dorseydouncestably.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Enzyme Lab With Liver Answers"
Post a Comment